LLM
LLM - Applications
LLM - Applications - Chat UI
-
GitHub - oobabooga/text-generation-webui (opens in a new tab)
Doesn't support MCP server integration yet
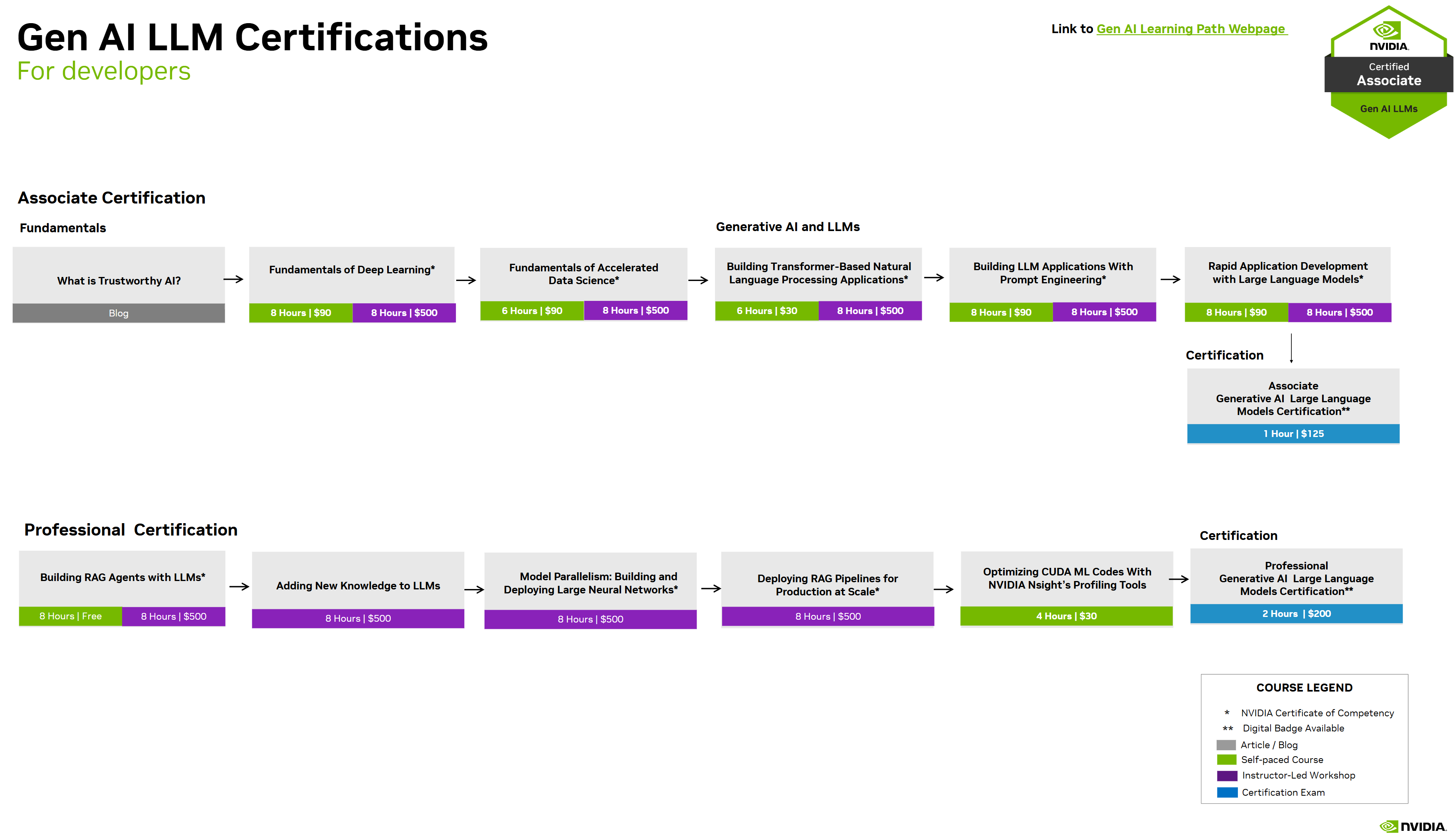
Certification
-
NVIDIA-Certified Associate - Generative AI LLMs
-
NVIDIA-Certified Professional - Generative AI LLMs
-
NVIDIA-Certified Professional - Agentic AI
-
NVIDIA-Certified Professional - Accelerated Data Science
Study target
AI Agent & Agentic AI Expertise
Advanced proficiency in AI agent frameworks (LangChain, LangGraph, AutoGen, CrewAI, or similar).
Deep understanding of multi-agent systems, agent communication protocols, and coordination mechanisms.
Extensive experience with Large Language Models (LLMs) and their integration into agent workflows.
Expert-level prompt engineering and chain-of-thought reasoning implementation.
Proven experience with autonomous agent architectures (ReAct, Plan-and-Execute, Reflection patterns).
Knowledge of agent memory systems, tool integration, and environment interaction.
AI-assisted Development Workflow
- Coding agent
Cheat sheet
Cheat sheet - Downloading models from Hugging Face
-
Ensure Git LFS is installed.
git lfs install -
Clone the model repo
# e.g. MODEL_ID=Qwen/Qwen3-8B-GGUF git clone https://huggingface.co/$MODEL_ID
Cheat sheet - Model reference
Framework for LLM use case evaluation
| Type of customer need | Example | ML Implementation (Yes/No/Depends) | Type of ML Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repetitive tasks where a customer needs the same output for the same input | Add my email across various forms online | No | Creating a rules-based system is more than sufficient to help you with your outputs |
| Repetitive tasks where a customer needs different outputs for the same input | The customer is in “discovery mode” and expects a new experience when taking the same action: - Generate a new artwork per click - StumbleUpon style exploration | Yes | - Image generation LLMs - Recommendation algorithms (collaborative filtering) |
| Repetitive tasks where a customer needs the same/similar output for different inputs | - Grading essays - Generating themes from customer feedback | Depends | If simple: rules-based system works. If complex combinations: - Classifiers - Topic modelling Use LLMs for patternless or one-off cases |
| Repetitive tasks where a customer needs different outputs for different inputs | - Answering customer support questions - Search | Yes | Too many permutations for rules-based systems. Consider: - LLMs with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) - Decision trees for products such as search |
| Non-repetitive tasks with different outputs | Review of a hotel/restaurant | Yes | Pre-LLMs needed specialized models: - Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) - LSTMs LLMs are a great fit for this type of scenario |
LLMOps
-
GitHub - tensorchord/Awesome-LLMOps (opens in a new tab)
An awesome & curated list of the best LLMOps tools for developers.
LLMOps - API
-
Gist
- Most LLM providers have an API compatible with OpenAI API.
-
Resources
API - Model Provider
-
Gist
- Local models
-
Providers
-
vLLM
-
KoboldCpp
- Forked from
llama.cpp, optimized for serving LLMs via an API. Kobold APIon port5001athttp://localhost:5001/api/OpenAI Compatible APIon port5001athttp://localhost:5001/v1/
- Forked from
-
-
Resources
API - API Gateway
-
Requirements
- Must be able to integrate custom OpenAI API compatible endpoints.
-
Providers
Coding agent
-
Providers
- aider (opens in a new tab) - CLI based, working on all platforms
-
Workflow
- Create a feature branch
- Create a plan / roadmap in markdown - either manually or chat to LLM to create and flesh it out.
- Then work through the plan, making frequent commits in local feature branch. You can go step by step (my approach, lets me micro manage / write code where its quicker for me than the llm), or just YOLO and ask Sonnet 3.7 / Gemini 2.5 pro to try and one shot (probably not a good idea if you are actually a developer, but the option is there!)
- Commit messages are unimportant, "WIP" is fine, its just the local branch, and enables easy rollbacks.
- You can of course follow changes in the terminal, but using the git window > local changes is often helpful, if you are following the step by step approach.
- When done, squash merge the local feature branch, writing a meaningful, semantic commit message
Concepts
Context length
The maximum number of tokens that an LLM can process in a single input sequence.
In simpler terms, context length acts as the model’s attention span determining how much information it can consider at once when generating responses.
-
GitHub - NVIDIA/RULER (opens in a new tab)
RULER: What’s the Real Context Size of Your Long-Context Language Models?
Training
Training - Pretraining
- Train the model on
a large corpus of text(raw text). Pretrainingcreates an initial pretrained LLM, called abaseorfoundationmodel.
Training - Fine-tuning
-
Train the model to
predict the next word in the textonlabeled data, akafine-tuning. -
2 most popular fine-tuning categories
-
Instruction fine-tuning
Labeled dataset consists of
instruction and answer pairs, such as a query to translate a text accompanied by the correct translation. -
Classification fine-tuning
Labeled dataset consists of
text and associated labels, such as emails withspamornot spamlabels.
-
Performance
Benchmark
Models
Pretrained Models (opens in a new tab)
Resources
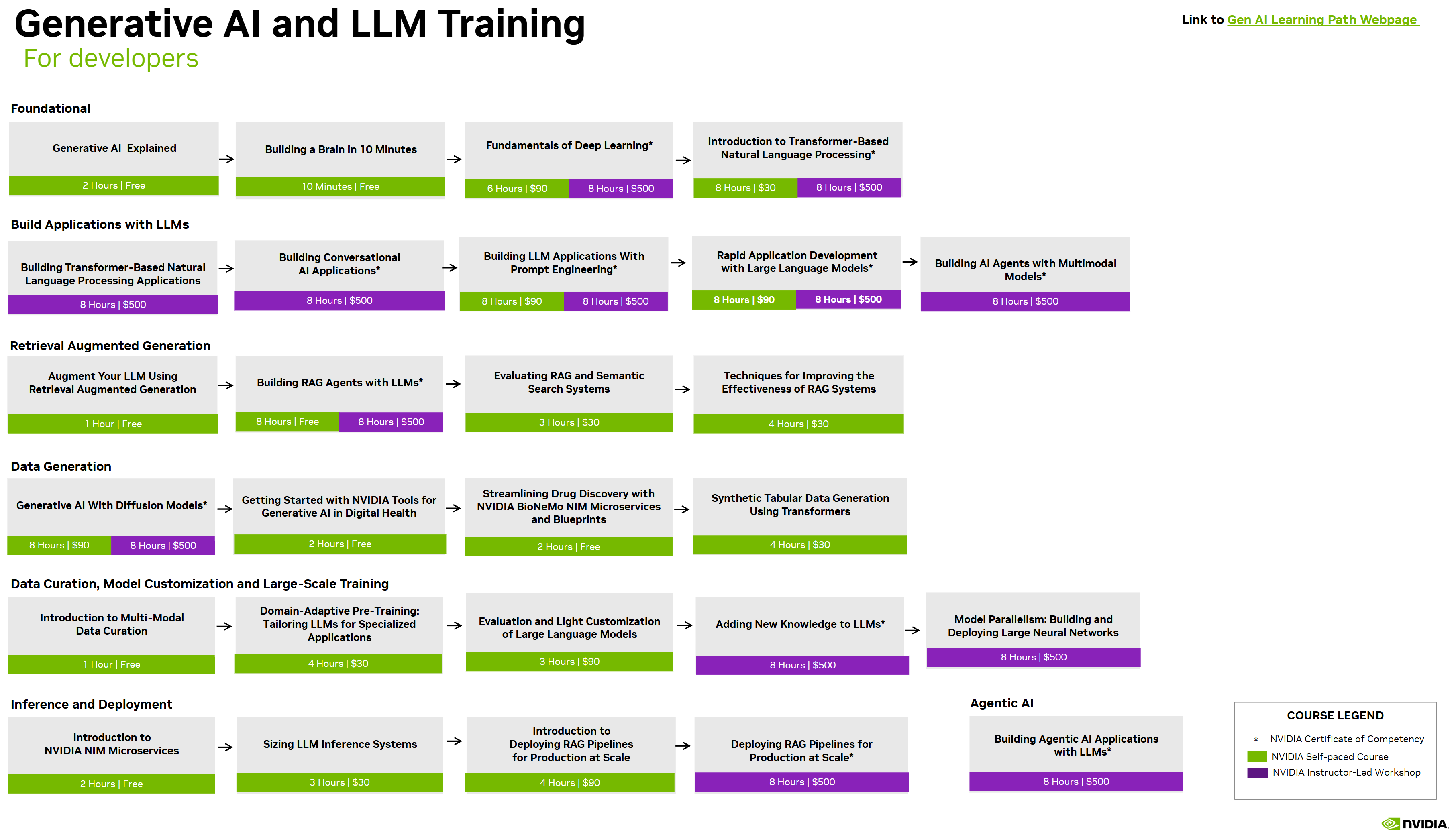
Learning Path
NVIDIA Generative AI LLM Learning Path (opens in a new tab)