Build - Dockerfile
- For each instruction in
Dockerfile,Dockerlooks to see if it already has an image layer for that instruction in its cache. If it does, this is a cache hit and it uses that layer. If it doesn’t, this is a cache miss and it builds a new layer from the instruction. Getting cache hits can hugely speed up the build process. - Use
multi-stagebuilds for smaller images and better security - As soon as any instruction results in a cache-miss (no layer was found for that instruction), the cache is no longer used for the rest of the entire build.
COPYandADDinstructions use file checksums to ensure that the content being copied into the image has not changed since the last build.
Dockerfile - Commands
FROM
-
The first instruction must be
FROM, which sets thebase imageto start from. -
Multi-stagebuild can have multipleFROMstatements.
ARG
-
Define variables to be used in
Dockerfile. -
Variable values can be supplied at build time via CLI:
# e.g. dbl --build-arg JAVA=jdk
WORKDIR
- Performs
mkdirandcdimplicitly in theimage
COPY
- The absolute path of your resources refers to an absolute path within the build context, not an absolute path on the host.
- Can only be used for local files and directories.
- Preferred to use over
ADD - Docker ADD vs. COPY: What are the Differences? (opens in a new tab)
ADD
- Officially discouraged to use
- Source can be a local file or directory, and a directory will be copied recursively.
- Source can also be a
URL. - A compressed archive as source can be automatically extracted in the given destination.
- The
srcpath must be inside the context of the build; you cannotADD ../something /something, because the first step of a docker build is to send the context directory (and subdirectories) to the docker daemon.
CMD
- Default command for when running a
container - If you list more than one
CMDthen only the lastCMDwill take effect. execform is preferred overshellform.- Typically used to supply default parameters to
ENTRYPOINT, which can be overridden from CLI parameters - If
ENTRYPOINTis absent,CMDwill be used as a command.
ENTRYPOINT
- The
ENTRYPOINTinstruction sets the executable to run at container startup. Dockerhas a defaultENTRYPOINTwhich is/bin/sh -cexecform is preferred overshellform, but it does not invoke a command shell. This means that normal shell processing such as variable and command substitution does not happen.- Usually not overriden at runtime, can only be overridden with
--entrypointflag
RUN
-
The
RUNinstruction will execute any commands in a new layer on top of the currentimageand commit the results. The resulting committedimagewill be used for the next step in theDockerfile. -
execform:RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo hello"]The
execform is parsed as aJSONarray, which means that you must use double-quotes (") around words not single-quotes (').
LABEL
- The
LABELinstruction adds key/value pairs to the image’s metadata.
EXPOSE
- The port on which the container listens on at runtime.
- Informational purpose, does not actually publish the port
VOLUME
-
Creates a mount point with the specified name
-
You must specify the host directory to mount when you create or run the container, but not when you build the image.
-
Resources
Dockerfile - Debug build
- Comment out the step that fails.
- Build the Dockerfile again.
- You will get an image with all the layers before the failed one.
- Use
diveto examine any step in question or usedocker run -itto navigate the container.
Build - CLI
Build an image
d build -t $repo_name/$image_name:$image_tag $relative_dockerfile_pathBuild an image with BuildKit
-
One-off
-
Run the build command with environment variable
DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1e.g.
$ DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build .Use
DOCKER_BUILDKIT=0will disable BuildKit. -
Alternatively, use
Docker BuildxCLI plugine.g.
$ docker buildx build .
-
-
Permanent
-
Linux:
/etc/docker/daemon.json{ "features": { "buildkit": true } } -
Windows / macOS: Use
Docker Desktopsettings
-
-
Resources
Display build logs with BuildKit
-
Run the build command with environment variable
BUILDKIT_PROGRESS=plaine.g.
BUILDKIT_PROGRESS=plain docker-compose build
Tag a local image
d tag $SOURCE_IMAGE $TARGET_IMAGETo push a new tag to a repository
d push $user_name/$repo_name:$image_tagRemove build cache
d builder pruneBuild - OCI Image
Docker in Docker
Cloud Native Buildpacks
-
Standardized SDK to turn source code into an image
-
Resources
Suggest builder based on existing code base
pack builder suggestBuild an image with pack CLI
pack build $image_name --builder $builder_nameJib (Java)
-
GitHub - GoogleContainerTools/jib (opens in a new tab)
Containerize Java applications
Client - CLI
List images
d images / d image ls-
Options
-
-aList all images
-
-qDisplay
image IDonly
-
-
Ascending order by image size
dils | sort -k7 -h -
Ascending order by image name
dils | sort -k1
List images with filter(s)
-
Example 1
d images -f reference='confluentinc/*:*'If filtering with multiple
reference, output would give, either match A or B.REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE confluentinc/confluent-cli latest 734463176a4d 2 weeks ago 275MB confluentinc/cp-ksqldb-server 7.2.1 140d2ac32177 3 months ago 1.36GB confluentinc/cp-ksqldb-cli 7.2.1 287039530a46 3 months ago 857MB confluentinc/cp-schema-registry 7.2.1 afaac043dcc1 3 months ago 1.86GB confluentinc/cp-enterprise-control-center 7.2.1 3ef895a26b4e 3 months ago 1.23GB confluentinc/cp-server 7.2.1 2fa77493d25b 3 months ago 1.67GB confluentinc/cp-zookeeper 7.2.1 3f28db6a433d 3 months ago 782MB confluentinc/cp-kafka-rest 7.2.1 784b8061ad0c 3 months ago 1.76GB confluentinc/ksqldb-server 0.8.0 e67283e9949c 2 years ago 667MB -
Example 2
d images -f reference='docker.elastic.co/*/*:*'Asterisk cannot represent slash.
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch 8.4.3 ce2b9dc7fe85 2 weeks ago 1.26GB docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana 8.4.3 b14d91e49f3f 3 weeks ago 800MB docker.elastic.co/apm/apm-server 8.4.3 81b0ed053a8a 3 weeks ago 230MB docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch 6.3.0 56d3dc08212d 4 years ago 783MB
Remove image(s)
d rmi $IMAGE_IDRemove multiple images
d rmi $image1_id $image2_id ...List all containers
d ps -a / d container ls -aCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
63cd9c728e0f nginx:1.17.10 "nginx -g 'daemon of…" 4 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 0.0.0.0:9332->80/tcp sharp_hofstadter
PORTS:
<HOST_IP:HOST_PORT>-><CONTAINER_PORT>/<PROTOCOL>Only display container ID
dps -qRun a container
-
If a
commandis supplied, the specifiedcommandwill be invoked. -
If no
commandis supplied, thecommandspecified byCMDinstruction will be invoked. -
Image nameandtagmust follow the options -
Options
-
-dRun container in background and print
container ID -
-p <HOST_IP>:<HOST_PORT>:<CONTAINER_PORT>/<PROTOCOL>Expose container port to host, eg:
-p 127.0.0.1:80:8080/tcp -
-eSet environment variables
-
--rmAutomatically remove the
containerwhen it exits
-
docker run -d -p <[HOST_IP:]HOST_PORT>:<CONTAINER_PORT> --name <CONTAINER_NAME> -e <KEY>=<VALUE> <IMAGE>:<TAG> <COMMAND> <ARGS...>
Start a container
d start $container_name_or_idStop a container
d stop $container_name_or_idRemove container(s)
# Some running containers need to be stopped before they can be removed.
d rm $container_name_or_id ...Log into a container
d exec -it $container_name_or_id bashMake permanent changes to a container
docker exec -it $CONTAINER_NAME / $CONTAINER_ID bashapt install vimdocker container commit
Stop a container from auto restarting
d update --restart=no $container_name_or_idList ports of a container
d port $container_nameDisplay command line of a container
d container inspect $container_name | jq '.[].Config'Copy files between a container and host
-
Docker volumes cannot be accessed directly from host. They can only be mounted to containers. Alternatively, use
docker cpto copy files in and out. -
d cp <local_path> <CONTAINER>:<path>From host to container
-
d cp <CONTAINER>:<path> <local_path>From container to host
-
Files can only be copied from container and host, if there's no container, create a temp one by
d create --name <container-name> <IMAGE>
Hosting a local repository (opens in a new tab)
Start the registry automatically by using --restart=always
dr -d -p 5000:5000 --restart=always --name registry registry:2Push an image to the local registry running at localhost:5000
d tag ubuntu:16.04 localhost:5000/my-ubuntu
d push localhost:5000/my-ubuntuRegistry authentication
-
Authenticated registries are listed in
$HOME/.docker/config.json -
To reauthenticate,
docker login <registry_URL>
Export an image to a TAR file
d save $IMAGE_ID > $IMAGE_TAR_FILESave and load image(s) to and from a TAR file, optionally with compression
-
Note: image Tar only contains image layers, to examine files in image, need to use
d exportwith an existing container. -
Supported compression types:
gzipbzip2xz
# Export image(s) as a TAR file
> d save $image > ${file.tar}
# Export image(s) as a Gzipped TAR file
> d save $image | gzip > ${file}.tar.gz
# Load image(s) from a TAR file
> d load < ${file.tar}
# Load image(s) from a Gzipped TAR file
> d load < ${file.tar.gz}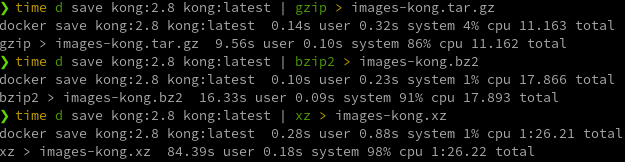
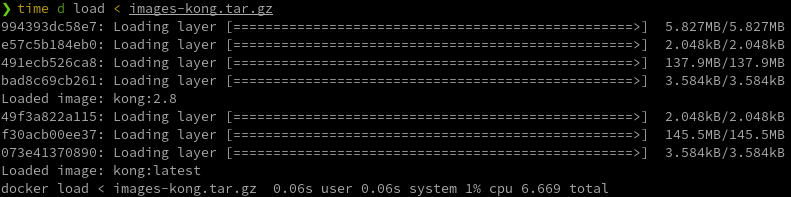
- Note: Use
repository:tagto reference Image, because usingImage IDwill make loaded image lose repository and tag.
Save and load images to STDOUT and from STDIN
d save $image | bzip2 | ssh $user@$host docker loadSave and load multiple images
# Retrieve all target image names (repo:tag)
> export IMAGES=$(d images \
-f reference='openapitools/*:*' \
-f reference='openzipkin/*:*' \
-f reference='pack.local/*/*:*' \
-f reference='jupyter/*:*' \
-f reference='paketobuild*/*:*' \
-f reference='jenkins/*:*' \
-f reference='grafana/*:*' \
-f reference='docker*/*/*:*' \
--format="{{.Repository}}:{{.Tag}}")
# Save images to TAR archive
> d save $IMAGES > ${file.tar}Examine file system in a image/container
-
Prepare the container of the image, if doesn't exist already
-
Export a container’s filesystem as a TAR archive
d export $container_name > ${file.tar}
Docker contexts - List available contexts
# The current one has asterisk after its name.
d context lsDocker contexts - Use another context
d context use $context_nameor
# This will override the current context
export DOCKER_CONTEXT=$context_nameDocker contexts - Create a new context
d context create ${context_name} \
--description ${description} \
--docker "host=$docker_endpoint"Docker contexts - Update a context
d context update $context_name --description "$description"Connect to a specified Docker daemon with different protocols
d -H $docker_endpoint $commandor
Use DOCKER_HOST environment variable
-
Protocols
- Unix domain socket:
unix:///var/run/docker.sock - Systemd socket activation:
fd:// - TCP:
tcp://192.168.59.106 - SSH:
ssh://me@example.com:22
- Unix domain socket:
List BOM of an image
d sbom $image:$tagCheck if a container is running
d ps -q -f name=$container_nameIf the container is running, container ID will be printed, otherwise no output.
Check the current storage driver
d info | grep -i storageDisplay the logs of a container
-
Display logs in stdout
d logs $container_nameor
dlo $container_name -
Save the logs to a file
d inspect --format='{{.LogPath}}' $container_nameor
dcin --format='{{.LogPath}}' $container_name
Display disk usage by Docker daemon
d system dfDisplay disk usage of different components in details
d system df -vDisplay disk usage of all volumes sorted by size
d system df --verbose --format '{{ range .Volumes }}{{ .Name }} {{ .Size }}\n{{ end }}' | sort -k2 -h | column -tDisplay volumes and mount points
d volume ls -q | xargs docker volume inspect --format '{{.Name}} {{.Mountpoint}}' | sort -k2 | column -tClean up build cache
d builder prunedocker - Send a SIGHUP to a container
d kill -s HUP $container_namedocker - Run curl in a container for troubleshooting
drit --rm curlimages/curl $arguments
# e.g. drit --rm curlimages/curl -s -v -X GET http://$host:$portClient - Docker Compose
-
Resources
-
Cheatsheet
-
View docker-compose file with rendered variables
dc config -
Pass env variables from shell to containers
# The value of the DEBUG variable in the container is taken from the value for the same variable in the shell in which Compose is run. web: environment: DEBUG: // Specify name only without value
-
-
By default Compose sets up a single network for your app. Each container for a service joins the default network and is both reachable by other containers on that network, and discoverable by them at a hostname identical to the container name.
-
Your app’s network is given a name based on the project name, which is based on the name of the directory it lives in. You can override the project name with either the
--project-nameflag or theCOMPOSE_PROJECT_NAMEenvironment variable. -
Control startup and shutdown order in Compose (opens in a new tab)
Add DNS entries for containers
kafka-http-cli-mvn:
image: cq-playground/pm-kafka-http-cli:latest
build:
extra_hosts:
host.docker.internal: 172.17.0.1Update image of a container with minimal downtime
-
Update image tag
-
Restart container
dcup -d --no-deps --build $service_name
Externalize environment variables
Server - Docker Daemon
- One daemon can expose multiple unix sockets
- Can be protected with TLS authentication
Daemon - Storage
-
Bind-mounts
- For sharing between the container and the host
- May have permission issues because of difference between container user and host user. Ensure that the directory on the host is accessible by the user inside the container
- Source directory must be absolute path.
-
Volumes
- Can be mounted to one or multiple containers, but not the host
- No permission issues
-
Resources
Daemon - Check which Daemon is active
# List all contexts, including the active one with **asterisk**
$ d context ls
NAME DESCRIPTION DOCKER ENDPOINT ERROR
default * Current DOCKER_HOST based configuration unix:///var/run/docker.sock
desktop-linux Docker Desktop npipe:////./pipe/dockerDesktopLinuxEngine
docker-ce Docker CE unix:///run/docker.sock# Inspect the active context
# In this case, assuming it is `default`
$ d context inspect default | jq
[
{
"Name": "default",
"Metadata": {},
"Endpoints": {
"docker": {
"Host": "unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
"SkipTLSVerify": false
}
},
"TLSMaterial": {},
"Storage": {
"MetadataPath": "<IN MEMORY>",
"TLSPath": "<IN MEMORY>"
}
}
]DOCKER_HOSTcan be used to override the active context.DOCKER_HOSTmust be set with an end point of the daemon.
Daemon - Get the current active daemon socket
d context ls --format json | jq -r 'select(.Current == true) | .DockerEndpoint'
> unix:///var/run/docker.sockDaemon - Test if a Daemon socket is accessible
# Suppose daemon socket is `/var/run/docker.sock`
$ curl -s -G --unix-socket /var/run/docker.sock http://localhost/version | jq{
"Platform": {
"Name": "Docker Desktop 4.0.0 ()"
},
"Components": [
{
"Name": "Engine",
"Version": "27.4.0",
"Details": {
"ApiVersion": "1.47",
"Arch": "amd64",
"BuildTime": "2024-12-07T10:38:57.000000000+00:00",
"Experimental": "false",
"GitCommit": "92a8393",
"GoVersion": "go1.22.10",
"KernelVersion": "5.15.167.4-microsoft-standard-WSL2",
"MinAPIVersion": "1.24",
"Os": "linux"
}
},
{
"Name": "containerd",
"Version": "1.7.21",
"Details": {
"GitCommit": "472731909fa34bd7bc9c087e4c27943f9835f111"
}
},
{
"Name": "runc",
"Version": "1.1.13",
"Details": {
"GitCommit": "v1.1.13-0-g58aa920"
}
},
{
"Name": "docker-init",
"Version": "0.19.0",
"Details": {
"GitCommit": "de40ad0"
}
}
],
"Version": "27.4.0",
"ApiVersion": "1.47",
"MinAPIVersion": "1.24",
"GitCommit": "92a8393",
"GoVersion": "go1.22.10",
"Os": "linux",
"Arch": "amd64",
"KernelVersion": "5.15.167.4-microsoft-standard-WSL2",
"BuildTime": "2024-12-07T10:38:57.000000000+00:00"
}Daemon - Access Docker Engine HTTP API
curl -s -G --unix-socket $docker_daemon_socket $docker_engine_api_endpoint | jq
# e.g.
curl -s -G --unix-socket /var/run/docker.sock http://localhost/version | jq-
Resources
Daemon - Display daemon details
curl -s -G --unix-socket $docker_daemon_socket http://localhost/info | jqAccess host in container
-
Docker Engine (Linux)
-
Use
host-gatewayor staticgateway IP, (In this example,172.17.0.1) for host, which is thegateway IPofbridgenetwork. To retrievegateway IP, rundocker network inspect bridge | jq '.[] | .IPAM.Config[] | .Gateway' -
Docker CLI
docker build --add-host "host.docker.internal:172.17.0.1" -t $image $relative_path_to_Dockerfile -
Docker Compose
build: context: $relative_path_to_Dockerfile dockerfile: $Dockerfile_name extra_hosts: host.docker.internal: 172.17.0.1 # alternatively, # extra_hosts: # host.docker.internal: host-gateway
-
-
Docker Desktop (Windows / Mac / Linux)
- Docker Desktop supports
host.docker.internalimplicitly, no need to addextra_hostsexplicitly.
- Docker Desktop supports
-
Troubleshooting
-
Check
/etc/hostsin the container to see if it contains entry for host gateway, e.g.:169.254.1.2 host.containers.internal host.docker.internalhost.containers.internalis supported byPodman.
-
-
Resources
Configure host gateway IP
Installation
Docker Engine
Docker Desktop
-
Linux
-
Start
systemctl --user start docker-desktop -
Stop
systemctl --user stop docker-desktop -
Sart on login
systemctl --user enable docker-desktop
WSL
-
Install Docker in WSL
Tools
Tools - dive (opens in a new tab)
-
Key Bindings
Key Binding Description Ctrl + CorQExit TabSwitch between sections Ctrl + FFilter files ESCClose filter files Page UporUScroll up a page Page DownorDScroll down a page Arrow UporKMove up one line within a page Arrow DownorJMove down one line within a page Ctrl + ALayer view: see aggregated image modifications Ctrl + LLayer view: see current layer modifications SpaceFiletree view: collapse/uncollapse a directory Ctrl + SpaceFiletree view: collapse/uncollapse all directories Ctrl + AFiletree view: show/hide added files Ctrl + RFiletree view: show/hide removed files Ctrl + MFiletree view: show/hide modified files Ctrl + UFiletree view: show/hide unmodified files Ctrl + BFiletree view: show/hide file attributes Page UporUFiletree view: scroll up a page Page DownorDFiletree view: scroll down a page
dive - Run dive Docker image
docker run --rm -it \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
docker.io/wagoodman/dive $dive_argumentsdive - Inspect a Docker image with tag
dive $image_name:$tagdive - Inspect a Docker image with ID
dive $image_iddive - Inspect a Docker image with an image TAR archive
Image TAR archive can be created by docker save command.
dive --source docker-archive $path_to_image_tar_archiveTroubleshooting
-
Set
vm.max_map_countto at least262144Some image requires this setting to work, such as
Elasticsearch.Elasticsearch Guide - Install Elasticsearch with Docker (opens in a new tab)
Integration
Testcontainers
- For integration with Java projects, you can achieve similar effects to Docker Compose from Java code.
- Use methods of
org.testcontainers.containers.ContainerStateto confirm container state. Wait.forHealthcheck()refers to Dokcer's Healthcheck support. Image must implement Docker HEALTHCHECK (opens in a new tab) forContainerState.isHealthymethod to work.- Exposed ports will be mapped to random ports, and those random ports can be retrieved by
ContainerState.getMappedPort. Mapped random ports are the ports via which your other services would be communicating with this container. Therefore the config of port numbers must be specified dynamically to align with the randomness.
Testcontainers - Cheatsheet
Start containers in parallel
- Using
Startables.deepStart(container1, container2, ...).join()will start all containers in parallel.
Expose specific ports of a container
-
Container.withExposedPorts(java.lang.Integer... ports) (opens in a new tab)
Equivalent to
EXPOSE <port>inDockerfile
Get the mapped host port for the exposed container port
Explicitly map a host port to a container port
-
Container.setPortBindings(java.util.List<java.lang.String> portBindings) (opens in a new tab)
Equivalent to
-p <host-port>:<container-port>indocker runor
Equivalent to
portsindocker-compose.yml -
Resources
Testcontainers - Troubleshoting
Docker Compose integration
- Not enough documentation
- Containers end before the test starts
- Vanilla docker image works fine but not with Docker Compose
Testcontainers - Spring Boot
Apache Maven
-
Use Maven Docker image (opens in a new tab)
-
Pros
settings.xmlcan be deployed together in the image, therefore simplifying repo config.
-
Cons
-
Caching artifacts
-
Options
- Create a Docker volume with
.m2directory in it and share the volume between containers
- Create a Docker volume with
-
-
-
Resources
-
Snyk Blog - 10 best practices to build a Java container with Docker (opens in a new tab)
-
Snyk Blog - 10 Docker Security Best Practices (opens in a new tab)
-
Quarkslab's blog - Why is Exposing the Docker Socket a Really Bad Idea? (opens in a new tab)
-
GitHub - veggiemonk/awesome-docker (opens in a new tab)
A curated list of Docker resources and projects - Awesome-docker (opens in a new tab)
-
GitHub - hexops/dockerfile (opens in a new tab)
Dockerfile best-practices for writing production-worthy Docker images
-
GitHub - containers/buildah - Container Tools Guide (opens in a new tab)
List a number of related Open-source projects that are available on GitHub.com that operate on Open Container Initiative (OCI) images and containers.