Set up
To set up a Python project (for example, for unit testing), you can install Delta Lake using pip install delta-spark and then configure the SparkSession with the configure_spark_with_delta_pip() utility function in Delta Lake:
from delta import *
builder = pyspark.sql.SparkSession.builder.appName("MyApp") \
.config("spark.sql.extensions", "io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension") \
.config("spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog", "org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog")
spark = configure_spark_with_delta_pip(builder).getOrCreate()Design
-
File listing
- Store the
paths to Parquet filesin thetransaction logtoavoid performing an expensive file listing. Doesn’t need tolist all Parquet filesin the cloud object store tofetch their paths.
- Store the
-
Small file problem
- Data processing engines don’t perform well when
reading datasets with many small files. You typically want files that arebetween 64 MB and 1 GB. You don't wanttiny 1 KB files that require excessive I/O overhead.
- Data processing engines don’t perform well when
-
ACID transactions
-
Schema-on-write enforcement
Schema validation before allowing a write transaction to occur.
-
Schema evolution
-
Permissive approach
-
You can set the
mergeSchemaoption totrueto write to aDelta tableand enable data with amismatched schemato be appended. -
New columnswould be added withnullvalues populated. -
New rowswould be added withnullvalues populated.
-
Transaction Logs
-
Gist
- One transaction commit per file
- Under
_delta_logfolder
-
Resources
Transaction Protocol
Transaction logis the single source of truth, any client who wants to read or write to aDelta tablemust first query thetransaction log.Transaction logis an append-onlyJSONLformatWAL, and it providesACIDtransaction guarantees.
Checkpoint
- Checkpoint files save the entire state of the table at a point in time - in native Parquet format that is quick and easy for Spark to read.
- Avoid the need to process from the beginning of transaction logs to restore the state.
Optimistic Concurrency Control
-
Gist
- Assume most of the time there are not conflicts or conflicts are rare.
- Best-effort auto merging
- Decline commit if merging fails
-
Benefits
- Reduce disruption and user intervention
-
Process
- Record the starting table version.
- Record reads/writes.
- Attempt a commit.
- If someone else wins, check whether anything you read has changed.
- Repeat.
Time Travel / Data Versioning
Any table state can be reproduced by replaying the transaction logs.
Data Lineage
Data Layout
Operation - OPTIMIZE (opens in a new tab)
-
Solution
Suppose you have a dataset with 10,000 small files that are slow to query. You can compact these 10,000 small files into a dataset with 100 right-sized files.
-
Gist
- Data practitioners will commonly want to compact the small files into larger files with a process referred to as
small file compactionorbin-packing. - The optimization process is idempotent.
- Small file compaction doesn’t help much when the dataset is relatively small.
- By default,
Delta Laketargets1 GBfiles whenOPTIMIZEis run. - Configurable with
spark.databricks.delta.optimize.maxFileSize - Specify
predicatestoonly compact a subset of datato avoid processing data already been compacted.
- Data practitioners will commonly want to compact the small files into larger files with a process referred to as
-
Delta Lake Small File Compaction with OPTIMIZE (opens in a new tab)
Operation - Z Order (opens in a new tab)
-
Example
OPTIMIZE events WHERE date >= current_timestamp() - INTERVAL 1 day ZORDER BY (eventType) -
Gist
- Z Ordering your data reorganizes the data in storage and allows certain queries to read less data, so they run faster.
- If you expect a column to be
commonly used in query predicatesand if that column hashigh cardinality(that is, a large number of distinct values), then useZORDER BY. - You can also
Z Ordera Delta tableon multiple columns.Z Orderingthe table byid1andid2helps queries that filter onid1,id2, and bothid1andid2. - To be replaced by
liquid clustering(opens in a new tab)
Liquid Clustering (opens in a new tab)
-
Databricks - Use liquid clustering for tables (opens in a new tab)
-
Gist
-
Replaces table
partitioningandZ-ORDER -
Applies to both
streaming tablesandmaterialized views -
You can
redefine clustering keys without rewriting existing data. -
Liquid clusteringisincremental. (only new data needs to be clustered) -
To enable
liquid clustering, add theCLUSTER BYphrase to a table creation statement.CREATE TABLE table1(col0 INT, col1 string) CLUSTER BY (col0); -
Automatic liquid clusteringallows Databricks tointelligently choose clustering keysto optimize query performance, using theCLUSTER BY AUTOclause. -
Liquid clusteringis not compatible withHive-stylepartitioning andZ-ordering. You may want to avoid liquid clustering if downstream systems requireHive-stylepartitioning. -
You can specify
up to 4clustering columnsper Delta table. -
Your clustering columns need to be
columns with statistics collected in the Delta logs. -
You can manually trigger a
liquid clustering operationusing theOPTIMIZEcommand. -
When you change the clustering columns, all new data writes and
OPTIMIZEoperations will follow the new clustering columns. Existing data is not rewritten.
-
-
Use cases
- Tables that are often filtered by
high cardinality columns. - Tables that have
skewin data distribution. - Tables that
grow quicklyand require maintenance and tuning effort. - Tables that have
concurrent write requirements. - Tables that have
access patterns that change over time. - Tables where a typical partition key could leave the table with
too many or too few partitions.
- Tables that are often filtered by
Operation - VACUUM
-
You can remove data files no longer referenced by a
Delta tablethat areolder than the retention thresholdby running theVACUUMcommand on the table. -
Default
retention periodis7 days. -
You
can't roll back the Delta Lake to a version that’s farther back than the retention periodif you’ve already run aVACUUMcommand. That’s why you need tobe careful before vacuuming your Delta Lake. -
Resources
Partition
-
Adding and Deleting Partitions in Delta Lake tables (opens in a new tab)
-
Pros and cons of Hive-style partitioning (opens in a new tab)
Delta Lake retrieves partition info from transaction logs instead of listing partition directories.
Schema
- Schema on write
- Delta Lake works out the final schema for the table by querying the transaction log, not by opening all the individual Parquet files. This makes schema evolution with Delta tables fast and more convenient for the user.
Schema Enforcement (opens in a new tab)
Prevents you from appending data with a different schema to a table unless you explicitly specify that the table should allow data with different schemas to be written.
-
Validation
- Cannot contain any additional columns that are not present in the target table's schema.
- Cannot have column data types that differ from the column data types in the target table.
- Can not contain column names that differ only by case.
-
Use cases
Schema evolutioncan be usedanytime you intend to change the schemaof your table (as opposed to where you accidentally added columns to yourDataFramethat shouldn't be there). It'sthe easiest way to migrate your schemabecause itautomatically adds the correct column names and data types, without having to declare them explicitly.
Schema Evolution (opens in a new tab)
-
Manual schema evolution
df.write .option("mergeSchema", "true") .mode("append") .format("delta") .save( "tmp/fun_people" ) -
Auto schema evolution
spark.conf.set("spark.databricks.delta.schema.autoMerge.enabled", "true")
Logical column names
Delta Lake abstracted the concept of physical column names and logical column names. The physical column name is the actual column name in the Parquet file. The logical column name is the column name humans use when referencing the column.
Delta Lake lets users quickly rename columns by changing the logical column name, a pure-metadata operation. It’s just a simple entry in the Delta transaction log.
Dropping columns
You can add an entry to the Delta transaction log and instruct Delta to ignore columns on future operations - it’s a pure metadata operation.
Change Data Feed (CDF) (opens in a new tab)
Change Data Feed (CDF) allows you to automatically track Delta table row-level changes.
Delta Sharing (opens in a new tab)
-
Gist
-
Share
A share is a logical grouping to share with recipients. A share can be shared with one or multiple recipients. A recipient can access all resources in a share. A share may contain multiple schemas.
-
Schema
A schema is a logical grouping of tables. A schema may contain multiple tables.
-
Table
A table is a Delta Lake table or a view on top of a Delta Lake table.
-
Recipient
A principal that has a bearer token to access shared tables.
-
Sharing Server
A server that implements this protocol.
-
-
Resources
Delta Sharing - REST API Protocol (opens in a new tab)
Delta Sharing - Databricks-to-Databricks Sharing (opens in a new tab)
Lets you share data from your Unity Catalog-enabled workspace with users who also have access to a Unity Catalog-enabled Databricks workspace.
Delta Sharing - Delta Sharing open sharing protocol (for providers) (opens in a new tab)
References
Delta Lake Documentation
- Deployed at Delta Lake Documentation (opens in a new tab)
- Source code at github.com/delta-io/delta-docs (opens in a new tab)
Delta Transaction Log Protocol (opens in a new tab)
Delta Table Specification (opens in a new tab)
DeltaOptions
DeltaSQLConf
-
org.apache.spark.sql.delta.sources.DeltaSQLConf (opens in a new tab)
Delta SQL configs
Delta Lake feature compatibility and protocols (opens in a new tab)
Compatibility with Apache Spark (opens in a new tab)
| Delta Lake version | Apache Spark version |
|---|---|
| 4.0.x | 4.0.x |
| 3.3.x | 3.5.x |
| 3.2.x | 3.5.x |
| 3.1.x | 3.5.x |
| 3.0.x | 3.5.x |
| 2.4.x | 3.4.x |
| 2.3.x | 3.3.x |
| 2.2.x | 3.3.x |
| 2.1.x | 3.3.x |
| 2.0.x | 3.2.x |
| 1.2.x | 3.2.x |
| 1.1.x | 3.2.x |
| 1.0.x | 3.1.x |
| 0.7.x and 0.8.x | 3.0.x |
| Below 0.7.0 | 2.4.2 - 2.4.<latest> |
Cheatsheet
Tables - Show table details (opens in a new tab)
Detail Schema (opens in a new tab)
DESC DETAIL @table_nameor
DESCRIBE DETAIL @table_nameTables - Show schema
DESC @table_nameor
DESCRIBE @table_name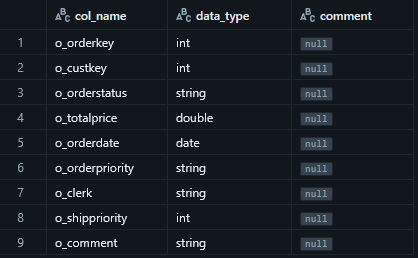
Tables - Show schema and detailed table info
DESC EXTENDED @table_nameor
DESCRIBE EXTENDED @table_name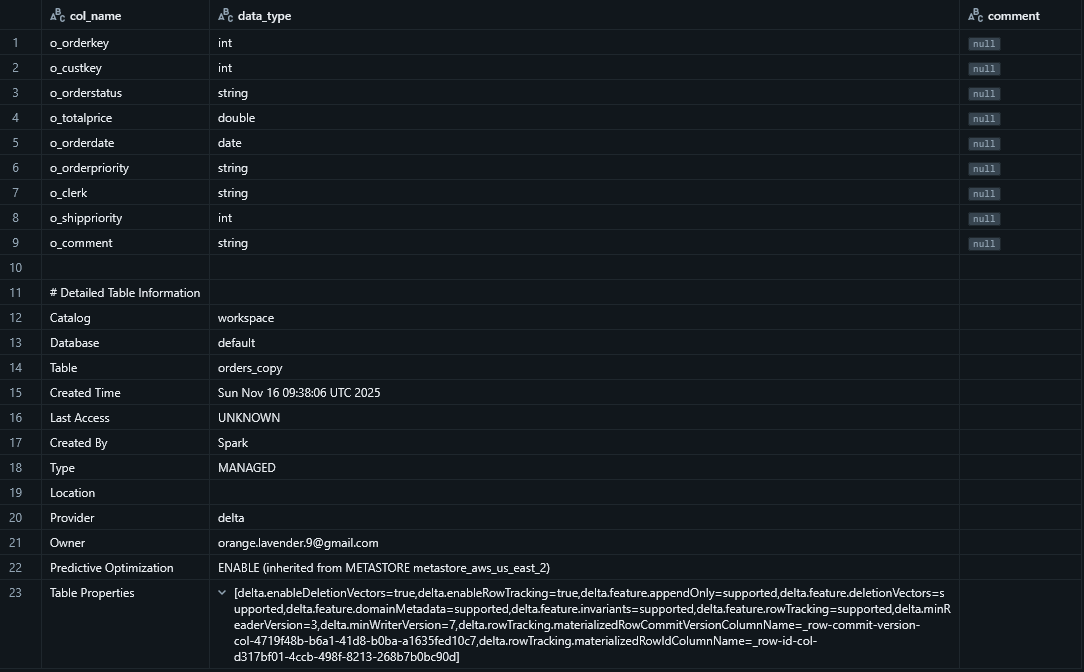
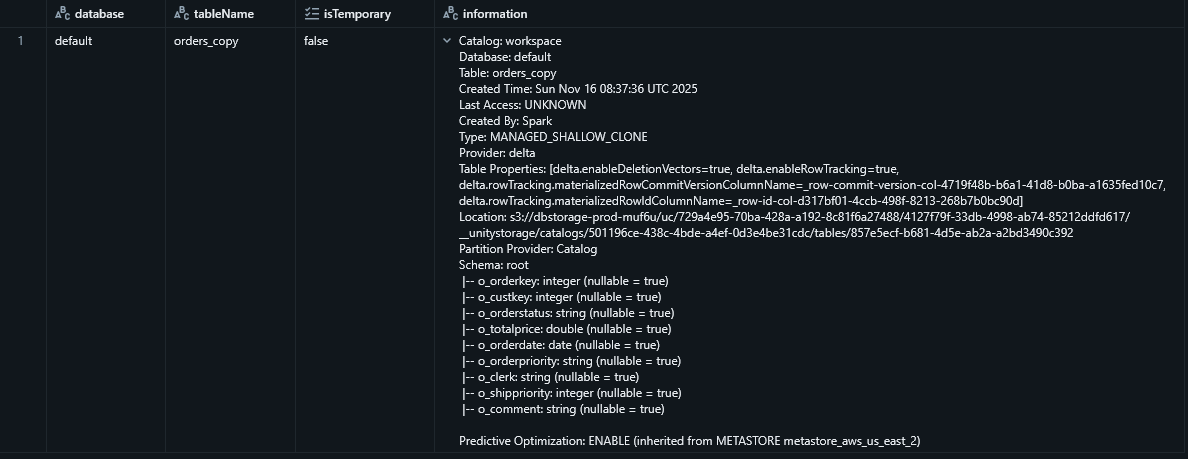
Tables - Shows information for all tables matching the given regular expression
SHOW TABLES EXTENDED IN @catalog_name LIKE @regexIncludes basic table information and file system information
Tables - Show table history (transaction logs)
DESC HISTORY @table_name;or
DESCRIBE HISTORY @table_name;Tables - Query a specific version of table
SELECT * FROM @table_name
VERSION AS OF @versionor
SELECT * FROM @table_name
VERSION@v<version>Tables - Query a specific version of table with a timestamp
SELECT * FROM @table_name
TIMESTAMP AS OF <timestamp_expression>Tables - Restore to a previous version of table / Time travel a table
RESTORE TABLE @table_name TO VERSION AS OF @versionor
RESTORE TABLE @table_name TO TIMESTAMP AS OF <timestamp_expression>Tables - Vacuum with a specified retention period
Example:
VACUUM @table_name RETAIN 0 HOURSTables - List all tables in default schema
SHOW TABLES;Tables - List all tables in the specified schema
SHOW TABLES IN @schema_name;Tables - List all tables in all catalogs
SHOW TABLES IN ALL CATALOGS;Tables - Create an external table
When creating an external table, you specify the location of the data files using the LOCATION keyword:
CREATE TABLE @table_name LOCATION @pathSince the metastore does not own the underlying data files, dropping an external table only removes the metadata associated with the table, leaving its data files intact.
Tables - Clone
-
Understanding CLONE Functionality in Databricks for Delta Tables (opens in a new tab)
-
Gist
Clone tables have their independent and new transaction logs, so any changes made to eitherdeeporshallowclonesaffect only the clones themselves and not the source table.- Can only make clones
- From
Managed TabletoManaged Table - From
External TabletoExternal Table - Error otherwise
- From
- Clones are only
statically sourcedfroma specific table version.
-
Use cases
- Data alignment between environments/teams.
- Editable copy of production data without copying the data (shallow clone).
- Disaster recovery: You can clone your table to a table in another cloud region after finishing a transaction(s).
Test your pipeline on production data: You can shallow clone your entire production data to a test environment and test your pipeline before release.- ML experiments on dev environment over
a snapshot of production data.
Tables - Clone - Deep
- Copies the source table data to the clone target in addition to the metadata of the existing table.
- Deep clones
do not depend on the source from which they were cloned, but are expensive to create because a deep clone copies the data as well as the metadata. Stream metadata is also clonedforsmooth migration from source table to the clone table.
Tables - Clone - Shallow
- Does not copy data files, and
reference data files in the source directory. - If you run
VACUUMagainst thesource tableand the files are out of the retention period of thesource tablebut are still referenced by otherclones, only the files that are not needed for either the source table or any clone will be removed. Shallow clone support for Unity Catalogallows you to create tables withaccess control privileges independent from their parent tableswithout needing to copy underlying data files.