Number Systems
- All numbers can be represented by the following format:
- Decimal:
735 = 700 + 30 + 5 = 7×10^2 + 3×10^1 + 5×10^0 - Binary:
10110 = 10000 + 0000 + 100 + 10 + 0 = 1×2^4 + 0×2^3 + 1×2^2 + 1×2^1 + 0×2^0 - Hexadecimal:
A3E = A00 + 30 + E = 10×16^2 + 3×16^1 + 14×16^0 - Therefore,
XYZ = X × <Base>^2 + Y × <Base>^1 + Z × <Base>^0 - This format also serves as the conversion from different bases to Decimal.
- Decimal:
Integer conversion
Fraction conversion
- See 1.8 Conversion between Two Number Systems with Fractional Part of Reference 1
Floating-Point Number Representation
-
Normalized form: There is only a single non-zero digit before the radix point.
For example, decimal number
123.4567can be normalized as1.234567×10^2; binary number1010.1011Bcan be normalized as1.0101011B×2^3. -
Convert decimal to binary:
- Convert the interger part to base 2
- Convert the fraction part to base 2
- Add two parts together and normalize the result
IEEE-754 32-bit Single-Precision Floating-Point Numbers
- Sign: 1 bit (31), 0 for positive, 1 for negative
- Exponent: 8 bit (23 - 30)
- Fraction: 23 bit (0 to 22)
Normalized form
- Exponent: from -126 to 127
- Fraction: an implicit leading 1 in the form of
1.F.
Decimal to Binary
Binary to Decimal
IEEE-754 64-bit Double-Precision Floating-Point Numbers
Data format
Text
URI
-
Percent encoding
-
Implementations
-
Java
java.net.URLEncoderjava.net.URLDecoder
-
-
Resources
Binary
- Encoding of binary data in a sequence of printable characters.
- For transmission of data when the channel does not allow binary data.
- Wikipedia - Binary-to-text encoding (opens in a new tab)
ASN.1
Object Identifier
-
OID describes the object. It is a series of nodes separated by period.
-
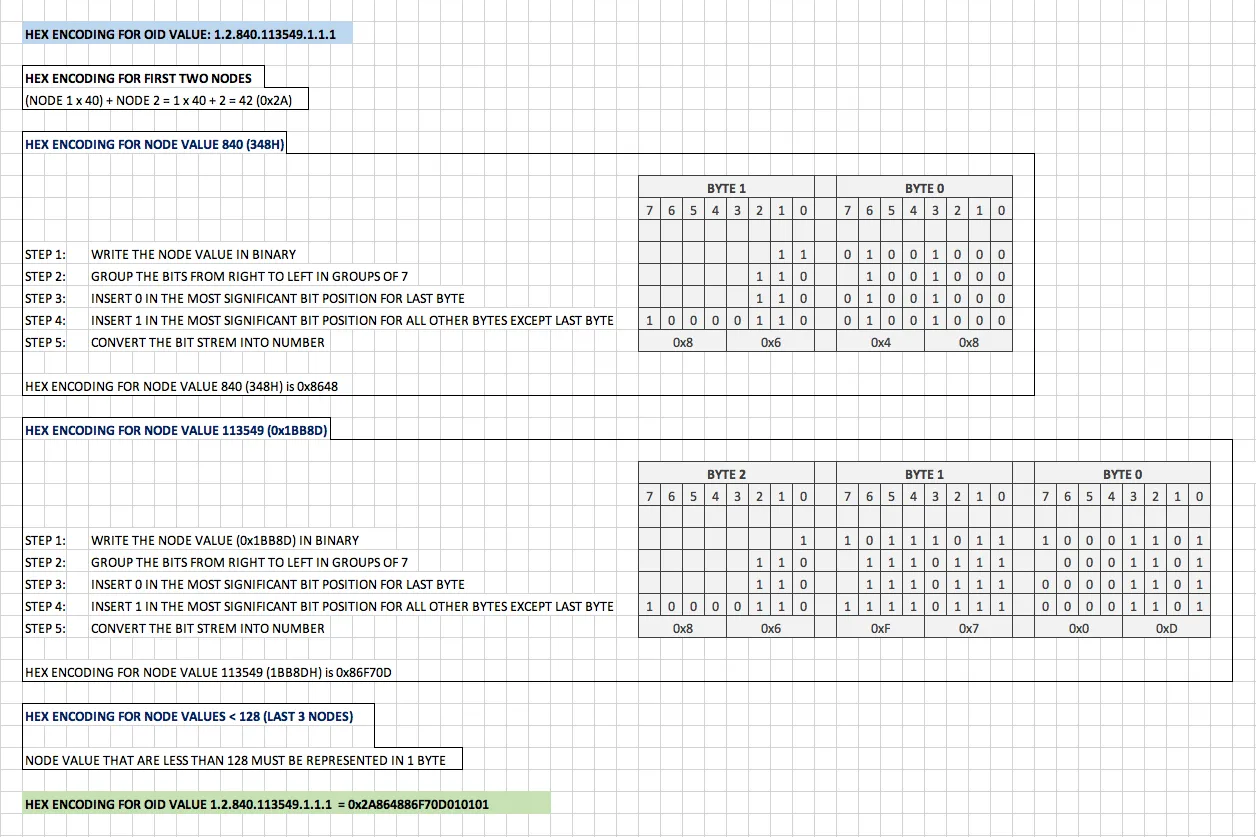
OID Value: 1.2.840.113549.1.1.1
-
OID description: Identifier for RSA encryption for use with Public Key Cryptosystem One defined by RSA Inc.
-
OID Encoding:
The first two nodes of the OID are encoded onto a single byte. The first node is multiplied by the decimal 40 and the result is added to the value of the second node. Node values less than or equal to 127 are encoded on one byte. Node values greater than or equal to 128 are encoded on multiple bytes. Bit 7 of all bytes except the rightmost byte is set to one. Bits 0 through 6 of each byte contains the encoded value.
-
OID Encoding Example:
-
Representing length in ASN.1 encoding
If number of value bytes is < 128 then length is represented in 1 byte. In this case most significant bit is 0. (Ex:- Line 2, Line 3 in structured DER content above) If number of value bytes is >= 128 then length is represented in multiple bytes. Most significant bit (bit 7) of first byte is 1 indicating multiple byte length. Bits 0–6 represent number of subsequent bytes for length. (Ex:- Line 1, Line 4 in structured DER content above)
-
Resources
Base64
-
Summary
Base64alphabet consists of64 characters, all of which are8-bit-padded ASCIIcharacters, and therefore printable.- The scheme is used to encode binary data with
ASCIIcharacters. - Every
3bytes (8bit each) of binary data are encoded to4ASCII printable characters, with every6bit represented a character, as per Wikipedia - Base64 table from RFC 4648 (opens in a new tab) MIMEspecifies a maximum line length of 76 characters.
-
Pros
- Used for protocol does not support
8-bit encoding. - Binary data that must be quickly verified by humans as a safety mechanism, such as file checksums or key fingerprints, is often represented in
Base64for easy checking.
- Used for protocol does not support
-
Cons
3bytes of data are encoded into4printableASCIIcharacters, which equals4bytes, a33%overhead (not including the overhead from headers)
-
References
Base62
-
Summary
Base62alphabet consists of62 characters, all of which are8-bit-padded ASCIIalphanumeric characters, and therefore valid for encoding URLs.
-
References
Cheatsheet
Convert a number from HEX to DEC in bash
> echo $((16#FF))
255
> printf "%d\n" 0xFF
255Convert JSON to Properties
yq -p json -o props $json_file > $properties_fileConvert YAML to Properties
yq -p yaml -o props $yaml_file > $properties_fileConvert JSON to YAML
yq -p json -o yaml $json_file > $yaml_fileConvert YAML to JSON
yq -p yaml -o json $yaml_file > $json_fileReference
- A Tutorial on Data Representation Integers, Floating-point Numbers, and Characters (opens in a new tab)
- Single-precision floating-point format (opens in a new tab)
- 单精度浮点数 (opens in a new tab)
- Double your money again - How to use BigDecimal or double for money (opens in a new tab)
- IEEE 754 (opens in a new tab)
- Floating-point arithmetic (opens in a new tab)
- Binary Fractions and Floating Point (opens in a new tab)
- Four common pitfalls of the BigDecimal class and how to avoid them (opens in a new tab)