Architecture
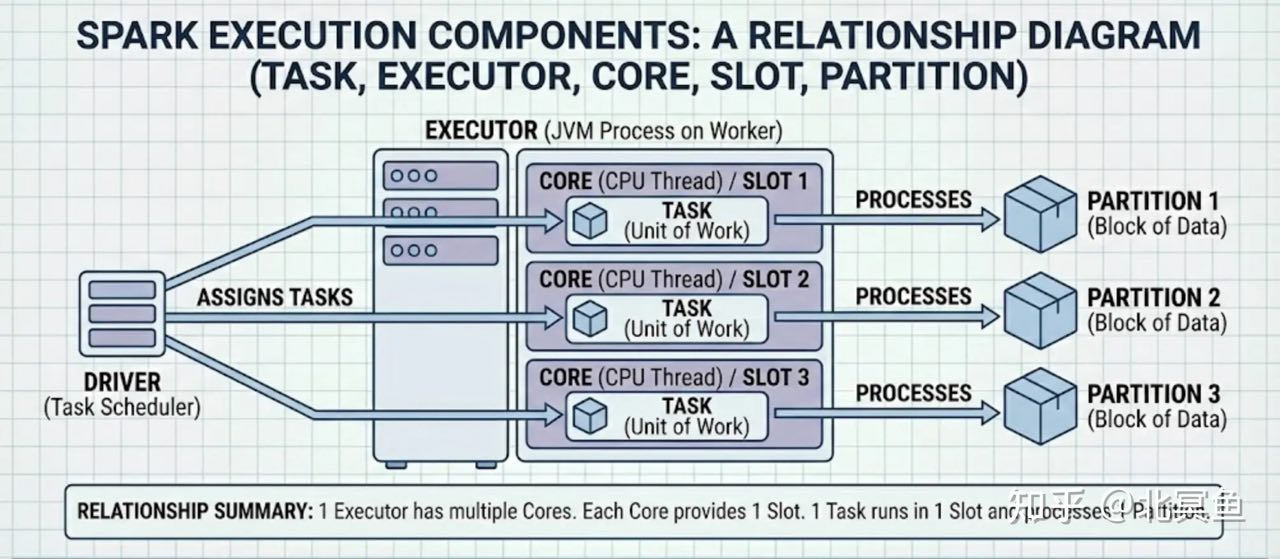
Driver
- The process running the
main()function of the application and creating theSparkContext - Contains the
SparkContextobject - Each application gets its own executor processes, which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads.
- Data cannot be shared across different Spark applications (instances of
SparkContext), meaning no inter-process sharing. - Because the
driverschedules tasks on the cluster, it should be runclose to the worker nodes,preferably on the same local area networkto minimize network latency between thedriversand theexecutors.
Driver - Deploy mode
-
Client (default)
locallyas an external client -
Cluster
deployed
on the worker nodes
Cluster Manager
-
Types
- Standalone
- Hadoop YARN
- Kubernetes
-
Master URL
-
Kubernetes
k8s://https://${k8s_apiserver_host}:${k8s_apiserver_port}
-
Playground
-
How to quickly set up a local Spark development environment (opens in a new tab)
Spark + Iceberg + Jupyter
Code
Deployment
Docker
Resources
AWS Prescriptive Guidance - Key topics in Apache Spark (opens in a new tab)
References
Reference - Apache Spark JIRA (opens in a new tab)
Reference - Spark - ScalaDoc (opens in a new tab)
Reference - Spark - Configuration (opens in a new tab)
PySpark
Reference - PySpark API Reference (opens in a new tab)
Reference - PySpark - Examples (opens in a new tab)
PySpark - Python Spark Connect Client
PySpark - Spark SQL and DataFrames
Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets Guide (opens in a new tab)
PySpark - Spark SQL API Reference (opens in a new tab)
PySpark - Pandas API on Spark
PySpark - Structured Streaming (opens in a new tab)
PySpark - Machine Learning (MLlib)
PySpark - Spark Core and RDDs
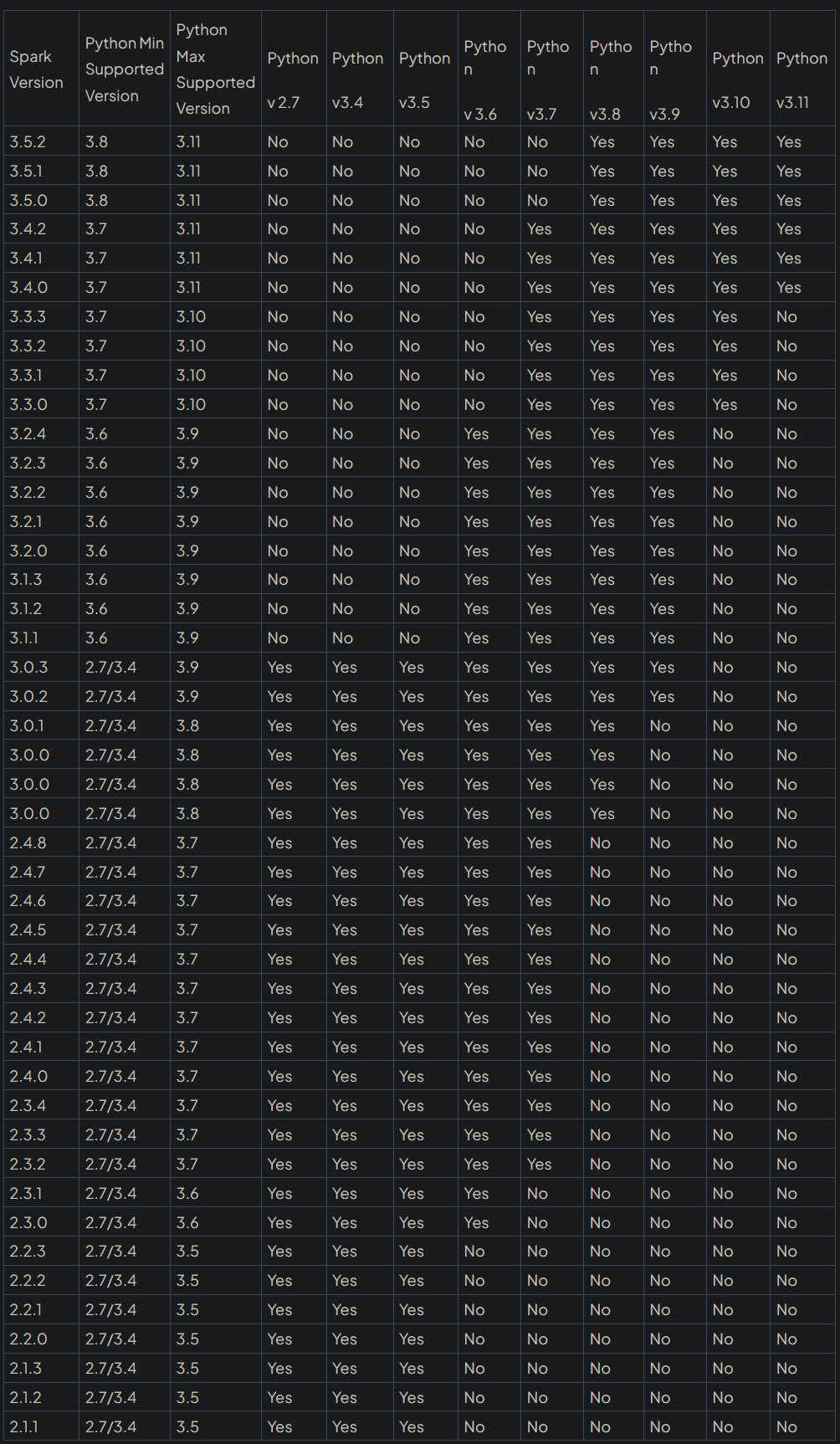
PySpark - Compatibility Matrix
Spark SQL
Spark SQL - Built-in Functions (opens in a new tab)
Global Temporary View (opens in a new tab)
Structured Streaming (opens in a new tab)
- Structured Streaming Programming Guide - API using Datasets and DataFrames
- Structured Streaming - PySpark API Reference (opens in a new tab)
- The Internals of Spark Structured Streaming (opens in a new tab)
Input Sources
-
Built-in sources
FilesourceKafkasourceSocketsource (testing)Ratesource (testing)RateperMicro-Batchsource (testing)
Stateful streaming (opens in a new tab)
-
A
statefulStructured Streaming queryrequires incremental updates tointermediate state information.- Streaming aggregation
- Streaming
dropDuplicates - Stream-stream joins
- Custom stateful applications
-
A
statelessStructured Streaming queryonly tracks information aboutwhich rows have been processedfrom the source to the sink.
Output mode (opens in a new tab)
- Only
stateful streamscontaining aggregations require anoutput modeconfiguration. - For
stateless streaming, alloutput modesbehave the same.
Append mode (default)
Only the new rows added to the Result Table since the last trigger will be outputted to the sink.
Complete mode
The whole Result Table will be outputted to the sink after every trigger. This is supported for aggregation queries.
Update mode
Only the rows in the Result Table that were updated since the last trigger will be outputted to the sink.
Streaming Joins (opens in a new tab)
Stream-Static Joins (opens in a new tab)
Inner joins
Left outer joins (left side is a streaming DataFrame)
Right outer joins (right side is a streaming DataFrame)
Stream-Stream Joins (opens in a new tab)
Trigger intervals (opens in a new tab)
Unspecified (default)
The query will be executed in micro-batch mode, where micro-batches will be generated as soon as the previous micro-batch has completed processing.
Fixed interval micro-batches
Exactly-onceguarantees- By default,
ProcessingTime=500ms
.trigger(processingTime='2 seconds')Available-now micro-batch
Exactly-onceguarantees- Replaces One-time micro-batch (
.trigger(once=True)) Consumes all available recordsinmultiple micro-batcheswithconfigurable batch size
# Deprecated
.trigger(once=True)
# Recommended
.trigger(availableNow=True)Continuous with fixed checkpoint interval
- Continuously process data as it arrives
Low (~1 ms) end-to-end latencywithat-least-once fault-tolerance guarantees.
.trigger(continuous='1 second')Checkpoints
-
Checkpointsandwrite-ahead logswork together to provide fault tolerance. -
checkpoint tracks the information that
identifies the query, includingstate informationandprocessed records. -
Each query must have a different checkpoint location.
-
Specifying
checkpointLocationoption will enable checkpointing.(df.writeStream .option("checkpointLocation", "/Volumes/catalog/schema/volume/path") .toTable("catalog.schema.table") )
Watermarking
-
Gist
-
Allow Spark to understand
when to close the aggregate windowand produce the correct aggregate result. -
Spark waits to close and output the
windowed aggregationoncethe max event time seen minus the specified watermark is greater than the upper bound of the window. -
Watermarks can only be used when you are running your streaming application in
appendorupdateoutput modes. -
You define a watermark by specifying
a timestamp field and a value representing the time threshold for late data to arrive.WATERMARK timestamp DELAY OF INTERVAL 3 MINUTES
-
-
Feature Deep Dive: Watermarking in Apache Spark Structured Streaming (opens in a new tab)
Spark Declarative Pipelines (SDP)
-
Gist
- Apache Spark
4.1+
- Apache Spark
-
Resources
SDP - Flows
- A flow is a
transformation relationship from source to target dataset. - Supports both
streamingandbatchsemantics SDPshares the same streaming flow type (Append,Update,Complete) asSpark Structured Streaming.
SDP - Datasets
Streaming Table
- Incremental processing to process only new data as it arrives
Materialized View
- Precomputed
- Always has exactly one batch flow writing to it
Temporary View
SDP - Pipelines
- A pipeline can contain one or more flows, streaming tables, and materialized views.
SDP - Pipeline Projects
- A
pipeline projectis a set ofsource filesthat contain code that define thedatasetsandflowsthat make up apipeline. - Source files can be
.pyor.sqlfiles. - Pipeline spec file by default is called
pipeline.yml.
SDP - Python
- SDP evaluates the code that defines a pipeline
multiple timesduringplanningandpipeline runs.Python functionsthat define datasets should includeonly the code required to define the table or view. - The function used to define a dataset must return a
Spark DataFrame. - Never use methods that
save or write to files or tablesas part of your SDP dataset code.
SDP - SQL
- The
PIVOTclause is not supported inSDP SQL. - When using the
for loop patternto define datasets inPython, ensure that the list of values passed to thefor loopisalways additive.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes - Kubeflow Spark Operator (opens in a new tab)
Local set up
-
Install a k8s cluster (k3d, minikube, kind, etc.)
-
Install Helm
-
Add Helm Repo
helm repo add spark-operator https://kubeflow.github.io/spark-operator helm repo update -
Install Spark Operator chart
helm install $release spark-operator/spark-operator \ --namespace $namespace \ --create-namespace -
Install a service account for Spark Operator
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubeflow/spark-operator/blob/master/config/rbac/spark-application-rbac.yaml -
Run a Spark application as demo
Ensure the name of the service account created in the previous step is used here.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubeflow/spark-operator/blob/master/examples/spark-pi.yaml -
Check the Spark application status
kubectl get sparkapp $spark_app_name -A
Kubernetes - Apache Spark Kubernetes Operator (opens in a new tab)
- Official project
- Younger project compared to Kubeflow
Catalog API
Performance Tuning
- Spark Docs - Performance Tuning (opens in a new tab)
- Spark Docs - Monitoring and Instrumentation (opens in a new tab)
- Top 10 code mistakes that degrade your Spark performance (opens in a new tab)
Join Strategies
- A given strategy may not support all join types, Spark is not guaranteed to use the
join strategysuggested by thejoin hint(opens in a new tab). - PySpark Joins: Optimize Big Data Join Performance | DataCamp
BROADCAST (Broadcast Join)
-
Use cases
- When each key within the smaller and larger data sets is hashed to the same partition by Spark
- When
one data set is much smaller than the other(and within the default config of 10 MB, or more if you have sufficient memory) - When you only want to perform an equi-join, to combine 2 data sets based on matching unsorted keys
MERGE (Shuffle Sort Merge Join)
-
Aliases
SHUFFLE_MERGEMERGEJOIN
SHUFFLE_HASH (Shuffle Hash Join)
SHUFFLE_REPLICATE_NL (Shuffle-and-replicate Nested Loop Join)
Bucketing
- Databricks - How to improve performance with bucketing (opens in a new tab)
- The 5-minute guide to using bucketing in PySpark
Spark UI
- Spark Web UI – Understanding Spark Execution (opens in a new tab)
- Databricks Docs - Debugging with the Spark UI (opens in a new tab)
- Spark Docs - Web UI (opens in a new tab)
Symptoms
Symptoms - Spill
Spillis what happenswhen Spark runs low on memory. It starts tomove data from memory to disk, and this can be quite expensive.- It is most common during
data shuffling.
Symptoms - Skew
Skewis when one or just a few tasks take much longer than the rest.- This results in
poor cluster utilizationandlonger jobs.
UDF
UDF - SQL (opens in a new tab)
-- Example
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION my_catalog.my_schema.calculate_bmi(weight DOUBLE, height DOUBLE)
RETURNS DOUBLE
LANGUAGE SQL
RETURN
SELECT weight / (height * height);Optimizations
Partitioning
| FEATURE | REPARTITION | COALESCE |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Adjusts the number of partitions, redistributing data across the specified number of partitions. | Reduces the number of partitions without shuffling data, merging existing partitions. |
| Full Shuffle | Yes | No |
| Expensiveness | Can be expensive, especially for large datasets, as it involves a full shuffle of data. | Less expensive than repartitioning, as it minimizes data movement by only combining partitions when possible. |
| Data Movement | Distributes data across partitions evenly, potentially leading to balanced partition sizes. | May result in imbalanced partition sizes, especially when reducing the number of partitions. |
| Use Cases | Useful when changing the number of partitions or evenly distributing data across partitions. | Useful when decreasing the number of partitions without incurring the cost of a full shuffle. |
Repartition
Redistributesdata across a specified number of partitions.- Very expensive operations as it shuffles the data across many partitions; hence, try to minimize using these as much as possible.
- When you call
repartition(n), wherenisthe desired number of partitions, Spark reshuffles the data in the RDD into exactlynpartitions. - If you
increase/decreasethe number of partitions usingrepartition(), Spark will perform afull shuffleof the data across the cluster, which can be an expensive operation, especially for large datasets.
Coalesce
Reduces the number of partitions without shuffling dataacross the cluster.- When you call
coalesce(n), wherenis the desired number of partitions, Sparkmerges existing partitions to create n partitions.
Apache Gluten
-
Gist
- Transform Spark’s whole stage physical plan to Substrait plan and send to native
- Offload performance-critical data processing to native library
- Define clear JNI interfaces for native libraries
- Switch available native backends easily
- Reuse Spark’s distributed control flow
- Manage data sharing between JVM and native
- Extensible to support more native accelerators