Open questions
- How to modularize a playbook?
Concepts
- Ansible uses
SSHby default for communication. Ansible Galaxyis a repository for third-party modules.- As a part of
Infrastructure as Codesolution,Ansibleshould be used for bootstraping the workflow, such as installing base packages on a bootstrap host. Inventorydefines the target hosts you wantAnsibleto run against.- The
commandmodule (and theshellmodule) execute your command in a child process.
Facts
Vault
- Red Hat - Sysadmin - How to encrypt Bash shell variables with Ansible Vault (opens in a new tab)
- How to set and use sudo password for Ansible Vault (opens in a new tab)
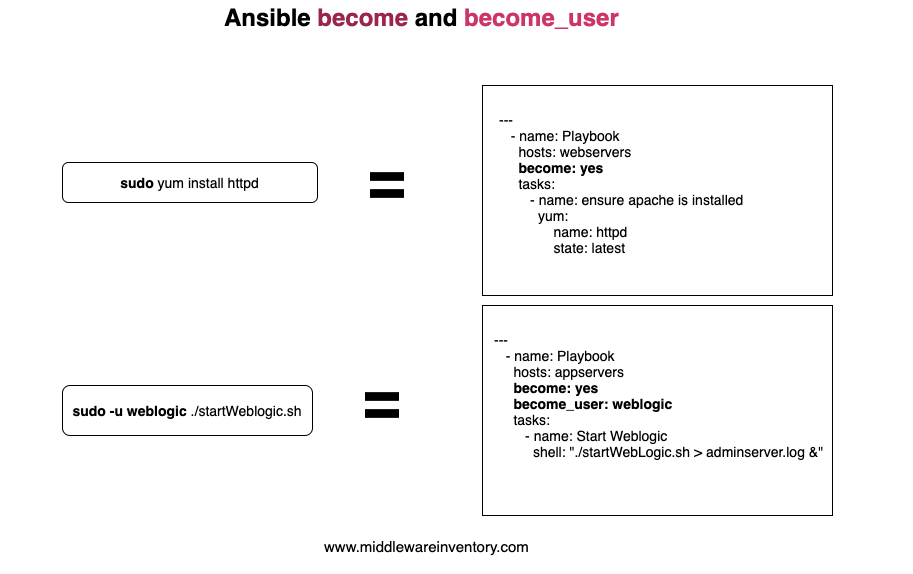
Privilege Escalation
Inventory
-
There are two default groups:
allandungrouped. -
To make use of existing
SSH config, inventory host name must match what's defined in theSSH config.# ~/.ssh/config Host ctfb_wsl_debian HostName localhost Port 2222 User takechiyo IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_wsl_debian IdentitiesOnly yes PasswordAuthentication no# Use the host defined in ~/.ssh/config [ctfb_wsl] ctfb_wsl_debian
SSH Connection
Prerequisites
-
SSH client configured on control host
- Generate public/private key pairs
- Deploy public key with
ssh-copy-idto target hosts / or append public key content toauthorized_keyson target host - Verify
SSHaccess
-
SSH server configured on target hosts
- Install
openssh-server - Enable
SSH portin/etc/ssh/sshd_config - Start
sshdservice:sudo service ssh start - Verify the service is running:
service ssh status
- Install
-
Ansible Collectionsused by Playbooks installed on control hostansible-galaxy collection list | grep <collection>ansible-galaxy install <collection>
Cheatsheet
List all avaiable plugins
ansible-doc -t $plugin_type -lList all available connection plugins
ansible-doc -t connection -lDisplay Ansible facts of target hosts
ansible ${host_pattern} -m setupansible all -m setup -a "filter=${fact_name}"-
Resources
Run an ad-hoc command on target hosts
ansible $host_pattern -a "$module_arguments"default module is command
e.g. ansible all -a "ip a"
Create a dedicated provisioning user on target hosts
# Generate SHA-512 hash from password input
password_hash=$(openssl passwd -6 $password_in_plain_text)
# Supply user name and password hash to create the user
ansible $host_pattern -kKbm user -a "name=$username password=$password_hash"Set up sudo access for the provisioning user on target hosts
# Suppose the user is called provisioning
# Create a sudoer definition file
echo "provisioning ALL=(root) NOPASSWD: ALL" > sudoer-provisioning
# Check syntax errors of the sudoer definition file
sudo visudo -cf sudoer-provisioning
# Deploy the sudoer definition file
ansible $host_pattern -kKbm copy -a "src=sudoer-provisioning dest=/etc/sudoers.d/sudoer-provisioning"Set up SSH authentication for the provisioning user on target hosts
# Deploy public key to target hosts for the specified user "provisioning"
ansible $host_pattern -kKbm authorized_key -a "user='provisioning' state='present' key='{{ lookup('file','<public-key-file-local-path>')}}'"
# Test access without interaction
ansible all -bm authorized_key -a "user='ansible' state='present' key='{{ lookup('file','<public-key-file-local-path>')}}'"Generate an example config
-
with all defaults
ansible-config init -t all > ansible.cfg -
with all defaults commented out
ansible-config init --disabled -t all > ansible.cfg
Verify and list changed config
ansible-config dump --only-changedTest connection to hosts specified in inventory
ansible --private-key=$private_key -i $inventory_file -m ping $hostDry run a playbook
-
-CCLI flagansible/ansible-playbook -C -
check_modeoption in playbookAdd
check_mode: yesto atask
Diff changes
-D CLI flag, can be used with -C or not
ansible/ansible-playbook -D
Display more info with verbose mode
-v, -vv, -vvv for more verbosity, -vvvv to enable connection debugging
Print variable value with debug task
- name: Print variable oh_my_zsh_home
debug:
var: oh_my_zsh_homeAccess environment variables on remote hosts
- name: Debug environment variables
debug:
msg: "{{ ansible_env.PATH }}"Use third-party modules
-
Install collection
ansible-galaxy collection install $collection -
Specify collection for any task in playbook
- name: Install Homebrew & packages collections: - community.general -
Use a module of the collection without full name
- name: Install Homebrew Formulae homebrew: path: "{{ homebrew_home }}/bin" name: "{{ brew_packages }}" update_homebrew: yes upgrade_all: yes register: changed_pkgs
Display help on a specific module
ansible-doc ${module_name}View Vault encrypted file
ansible-vault view ${encrypted_file}Supply sudo password to escalate privilege
- Input password interactively
ansible-playbook --ask-become-pass $playbook- Supply password in command line
ansible-playbook -e "ansible_become_pass=$password" $playbookReferences
-
DigitalOcean - How to Use Ansible to Install and Set Up Docker on Ubuntu 20.04 (opens in a new tab)
To initiate a workflow revolving around
OCIimages,Docker Engineneeds to be installed in the beginning on the target host. -
Ansible Documentation - Special Variables (opens in a new tab)